In this article, we will implement a ReactJs(v18) CRUD example by creating state management using the Zustand library.
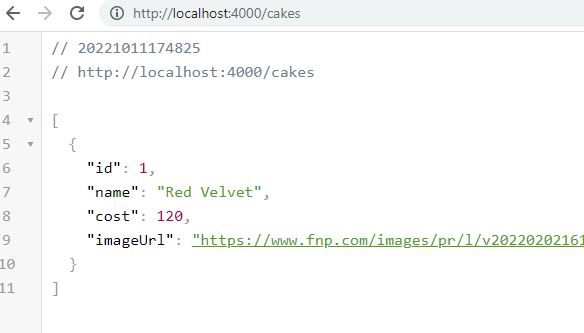
Now access our fake JSON API at 'http://localhost:4000/cakes".
Zustand:
The Zustand is a small, fast, and scalable state management library. It is straightforward to use and integrate. Some of its features are:
- It contains hooks API, so it is very easy to consume in react applications.
- Support for Async methods.
- Easily integrate additional middleware like 'immer', 'devtools', etc
- State can be accessed outside of the react components
- Easily integrate along with other state management libraries like 'Redux' & 'React Context API'.
Create ReactJS Application:
Let's create a ReactJS Application to accomplish the demo.
npx create-react-app name-of-your-app
Configure React Bootstrap Library:
Let's install the React Bootstrap library.
npm install react-bootstrap bootstrap
Now add the bootstrap CSS file reference on 'index.js'.
import 'bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css';
Create React Component 'Layout':
Now let's React component like 'Layout' inside of 'components/shared'(new folders). This 'Layout' component will be our master template where we can have a header and footer.
src/components/shared/Layou.js:
import { Container } from "react-bootstrap";
import Navbar from "react-bootstrap/Navbar";
const Layout = ({ children }) => {
return (
<>
<Navbar bg="primary" variant="dark">
<Navbar.Brand>Cakes</Navbar.Brand>
</Navbar>
<Container>{children}</Container>
</>
);
};
export default Layout;
- Here we configured the React Bootstrap Navbar component.
src/App.js:
import "./App.css";
import Layout from "./components/shared/Layout";
function App() {
return <Layout></Layout>;
}
export default App;
Create React Component 'AllCakes':
Let's create a page-level react component like 'AllCakes' inside of 'pages' folder(new folder).
src/pages/AllCakes.js:
const AllCakes = () => {
return <></>;
};
export default AllCakes;
Configure React Routing:
Install the 'react-router-dom' package.
npm i react-router-dom
Now configure the 'Routes' component in the 'App' component.
src/App.js:
import { Route, Routes } from "react-router-dom";
import "./App.css";
import Layout from "./components/shared/Layout";
import AllCakes from "./pages/AllCakes";
function App() {
return (
<Layout>
<Routes>
<Route path="/" element={<AllCakes />}></Route>
</Routes>
</Layout>
);
}
export default App;
- Here home page route is configured to the 'AllCakes' component.
src/index.js:
import React from "react";
import ReactDOM from "react-dom/client";
import "./index.css";
import App from "./App";
import "bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css";
import { BrowserRouter } from "react-router-dom";
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById("root"));
root.render(
<BrowserRouter>
<App />
</BrowserRouter>
);
Install Zustand Library:
Let's install our 'Zustand' state management library.
npm install zustand
Configure Store:
Let's try to configure a sample store. So let's create a folder like 'store' and then add a file like 'cakeStore.js'.
src/store/cakeStore.js:
import create from "zustand";
export const useCakeStore = create((set) => ({
cakesData: [
{
id: 1,
name: "Red Velvet",
cost: 120,
imageUrl:
"https://www.fnp.com/images/pr/l/v20220202161510/valentine-s-heart-red-velvet-cake_1.jpg",
},
]
}));
- (Line: 3) The 'create' method loads from the 'zustand' library. The 'set' input parameter helps to update the data into the state property.
- (Line: 4) The 'cakeData' is my store state property. Here assigned some sample data.
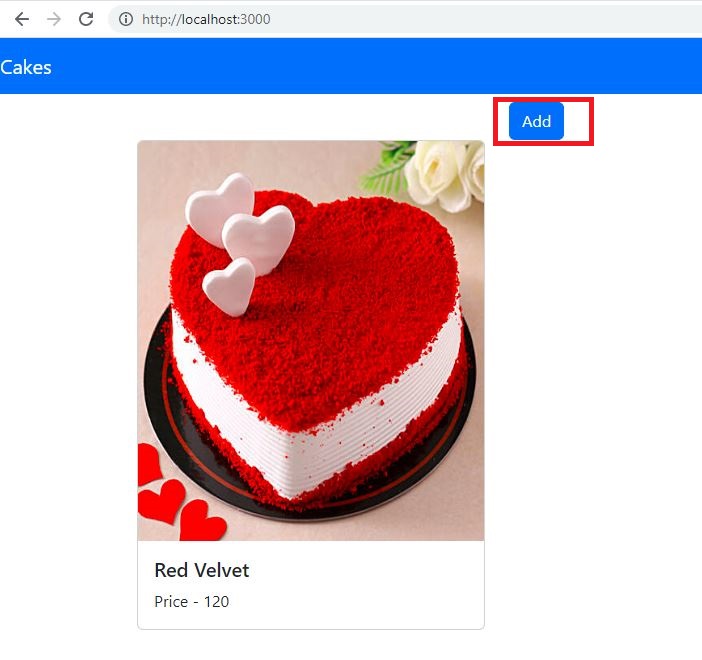
Implement Read Operation(Read Dummy Data From Store):
Let's implement the read operation by fetching the sample data from our store(cakStore.js).
src/pages/AllCakes.js:
import { Container,Row, Col,Card } from "react-bootstrap";
import { useCakeStore } from "../store/cakeStore";
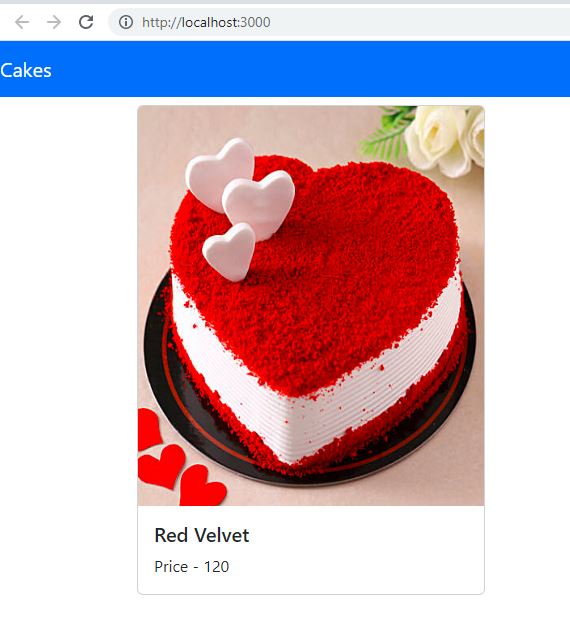
const AllCakes = () => {
const allCakes = useCakeStore((state) => state.cakesData);
return (
<>
<Container className="mt-2">
<Row xs={1} md={3} className="g-4">
{allCakes.map((cake) => (
<Col key={cake.id}>
<Card>
<Card.Img
variant="top"
src={cake.imageUrl}
style={{ height: 400, width: "100%" }}
/>
<Card.Body>
<Card.Title>{cake.name}</Card.Title>
<Card.Text>Price - {cake.cost}</Card.Text>
</Card.Body>
</Card>
</Col>
))}
</Row>
</Container>
</>
);
};
export default AllCakes;
- (Line: 5) The 'useCakeStore' is our store hook created using the 'zustand' library. So here we passed the arrow function with store 'state' as the input parameter and returns any state property or state action(function).
- (Line: 10) Here looping our 'allCakes' variable that got data from our store.
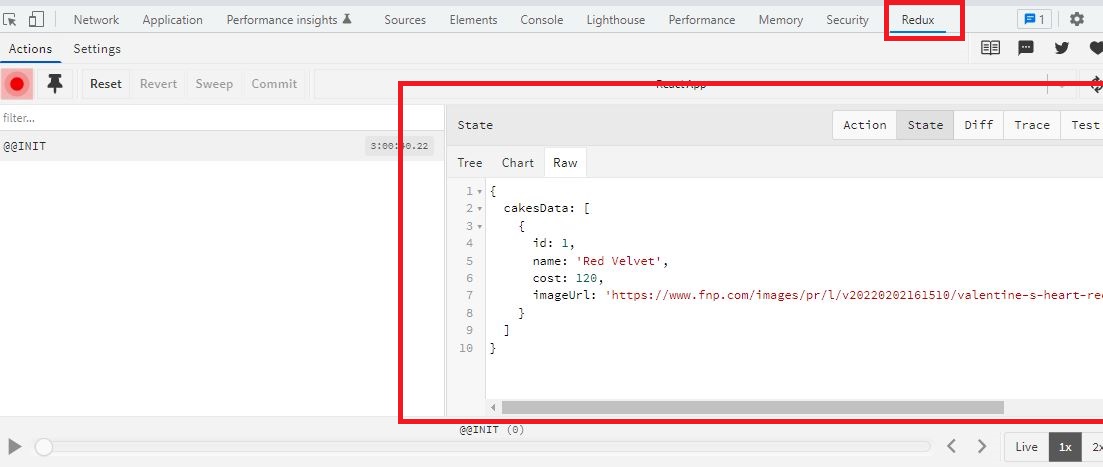
Configure DevTools:
Using Zustand store management we can use the 'DevTools' to track the changes of state in our 'Redux' browser extension tool.
src/store/cakeStore.js:
import create from "zustand";
import { devtools } from "zustand/middleware";
export const useCakeStore = create(
devtools((set) => ({
cakesData: [
{
id: 1,
name: "Red Velvet",
cost: 120,
imageUrl:
"https://www.fnp.com/images/pr/l/v20220202161510/valentine-s-heart-red-velvet-cake_1.jpg",
},
],
}))
);
- (Line: 5) Add the 'devtools' that loads from the 'zustand/middleware'.
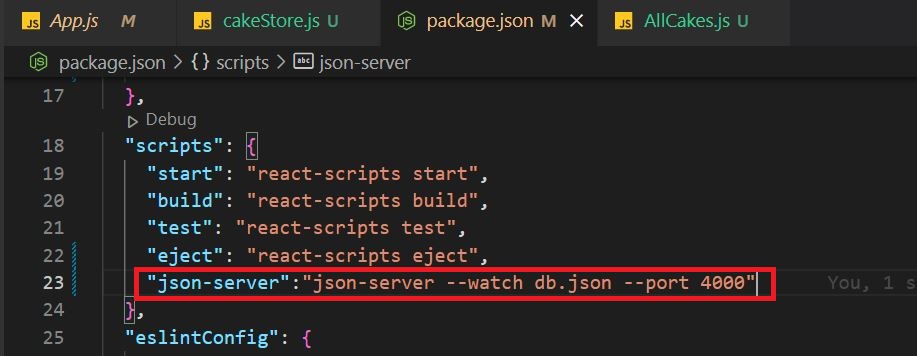
Setup JSON Server:
Let's setup the fake API by setting up the JSON server in our local machine.
Run the below command to install the JSON server globally onto your local machine.
npm install -g json-server
For our demo purpose go to the ReactJS application and add the following to the 'package.json' file. By default, the JSON server runs on port number 3000, ReactJS also runs on the same portal locally so here we specify another port number explicitly.
"json-server":"json-server --watch db.json --port 4000"
Now to invoke the above command run the following command in the ReactJS app root folder.
npm run json-server
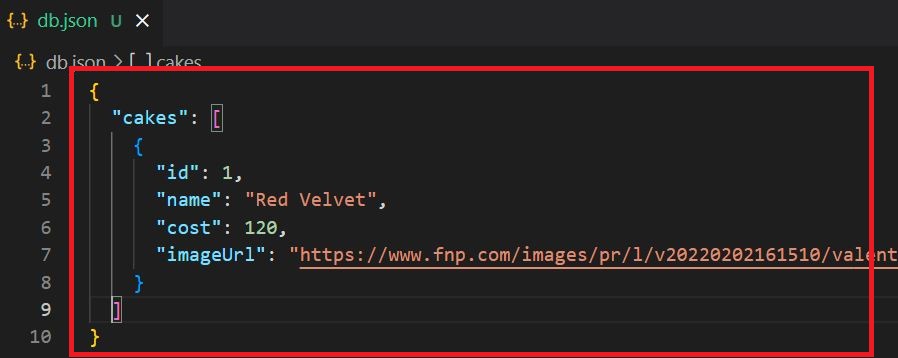
After running the above command for the first time, a 'db.json' file gets created, so this file act as a database. So let's add some sample data to the file below.
Install Axios Library:
Let's install the Axios library.
npm i axios
Implement Read Operation:
Let's implement the read operation by invoking the API and then saving the API response to the store and then fetching data from the store to our react component.
Using the Zustand store library we can invoke API calls in our store file 'cakeStore.js' as action methods.
src/store/cakeStore.js:
import create from "zustand";
import { devtools } from "zustand/middleware";
import { immer } from "zustand/middleware/immer";
import axios from "axios";
export const useCakeStore = create(
devtools(
immer((set) => ({
cakesData: [],
getApi: async () => {
const apiResponse = await axios.get("http://localhost:4000/cakes");
set((state) => {
state.cakesData = apiResponse.data;
});
},
}))
)
);
- (Line: 8) The 'immer' loads from the 'zustand/middleware/immer'. Here 'immer' helps to change the state data very easy way.
- (Line: 10-15) Using zustand, we can async or nonasync methods directly into the store. Here 'getAPI' method invokes the API call to fetch data.
- (Line: 12-14) Assigning the API response to our 'cakeData' state property.
src/pages/AllCakes.js:
import { useEffect } from "react";
import { Container, Row, Col, Card } from "react-bootstrap";
import { useCakeStore } from "../store/cakeStore";
const AllCakes = () => {
const allCakes = useCakeStore((state) => state.cakesData);
const callGetAPI = useCakeStore((state) => state.getApi);
useEffect(() => {
callGetAPI();
}, []);
return (
<>
<Container className="mt-2">
<Row xs={1} md={3} className="g-4">
{allCakes.map((cake) => (
<Col key={cake.id}>
<Card>
<Card.Img
variant="top"
src={cake.imageUrl}
style={{ height: 400, width: "100%" }}
/>
<Card.Body>
<Card.Title>{cake.name}</Card.Title>
<Card.Text>Price - {cake.cost}</Card.Text>
</Card.Body>
</Card>
</Col>
))}
</Row>
</Container>
</>
);
};
export default AllCakes;
- (Line: 7) Here we get the reference of our 'getAPI' method from our store.
- (Line: 10) Invoking the Api call.
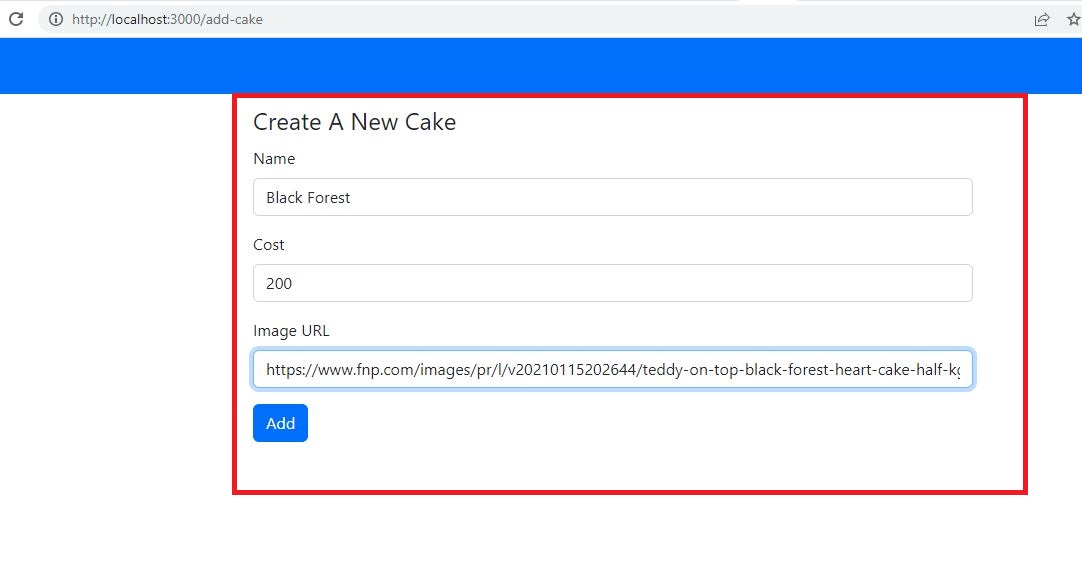
Create React Component 'AddCake.js':
Let's create a new React component like 'AddCake.js' in the 'pages' folder.
src/pages/AddCake.js:
const AddCake = () => {
return <></>;
};
export default AddCake;
Configure the route for 'AddCake' component in the 'App' componentsrc/App.js:
import { Route, Routes } from "react-router-dom";
import "./App.css";
import Layout from "./components/shared/Layout";
import AddCake from "./pages/AddCake";
import AllCakes from "./pages/AllCakes";
function App() {
return (
<Layout>
<Routes>
<Route path="/" element={<AllCakes />}></Route>
<Route path="/add-cake" element={<AddCake />}></Route>
</Routes>
</Layout>
);
}
export default App;
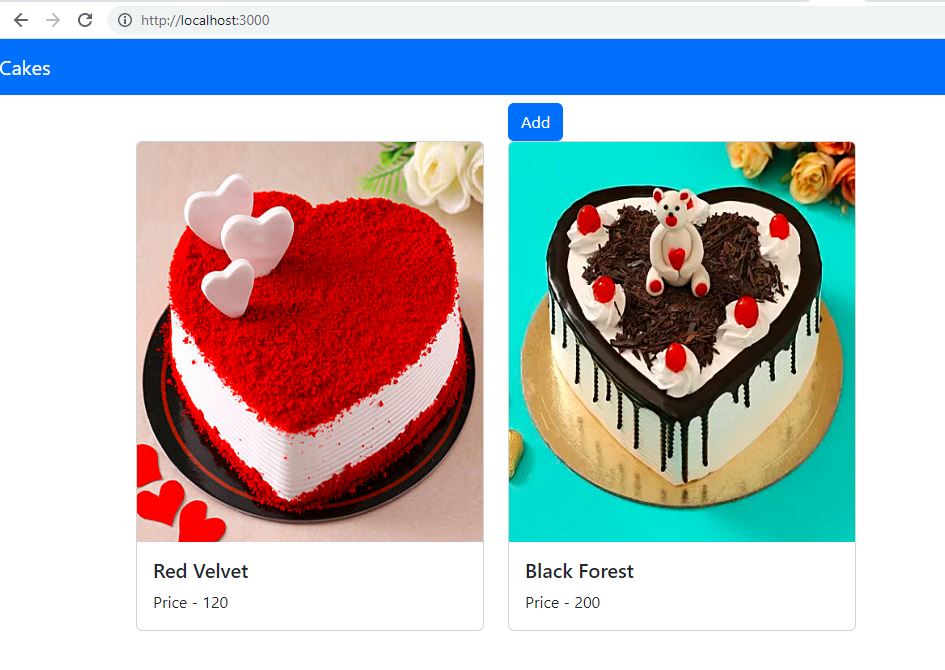
Implement Create Operation:
Let's implement the create operation by creating a new item and also updating the new item data in the store.
Let's implement the create API call in 'cakeStore.js'.
src/store/cakeStore.js:
import create from "zustand";
import { devtools } from "zustand/middleware";
import { immer } from "zustand/middleware/immer";
import axios from "axios";
export const useCakeStore = create(
devtools(
immer((set) => ({
cakesData: [],
getApi: async () => {
const apiResponse = await axios.get("http://localhost:4000/cakes");
set((state) => {
state.cakesData = apiResponse.data;
});
},
createCakeAPI: async (payload) => {
const apiResponse = await axios.post(
"http://localhost:4000/cakes",
payload
);
set((state) => {
state.cakesData.push(apiResponse.data);
});
},
}))
)
);
- (Line: 16-24) The 'createCakeAPI' method invokes our post API and response data is saved into the store.
src/pages/AddCake.js:
import { useRef } from "react";
import { Col, Container, Row, Form, Button } from "react-bootstrap";
import { useNavigate } from "react-router-dom";
import { useCakeStore } from "../store/cakeStore";
const AddCake = () => {
const name = useRef("");
const imageUrl = useRef("");
const cost = useRef("");
const createAPICall = useCakeStore((state) => state.createCakeAPI);
const navigate = useNavigate();
const createHanlder = async () => {
let payload = {
name: name.current.value,
imageUrl: imageUrl.current.value,
cost: Number(cost.current.value)
};
await createAPICall(payload);
navigate("/");
};
return (
<>
<Container className="mt-2">
<Row>
<Col className="col-md-8 offset-md-2">
<legend>Create A New Cake</legend>
<Form.Group className="mb-3" controlId="formName">
<Form.Label>Name</Form.Label>
<Form.Control type="text" ref={name} />
</Form.Group>
<Form.Group className="mb-3" controlId="formCost">
<Form.Label>Cost</Form.Label>
<Form.Control type="text" ref={cost} />
</Form.Group>
<Form.Group className="mb-3" controlId="formImageUrl">
<Form.Label>Image URL</Form.Label>
<Form.Control type="text" ref={imageUrl} />
</Form.Group>
<Button
variant="primary"
type="button"
onClick={createHanlder}
>Add</Button>
</Col>
</Row>
</Container>
</>
);
};
export default AddCake;
- (Line: 6-9) The 'useRef' variable is to read the form data.
- (Line: 12) Get the reference of the create API call method from the store.
- (Line: 15-23) The 'createHandler' method reads our form data and sends it to the create API call as payload.
src/page/AllCakes.js:
import { useEffect } from "react";
import { Container, Row, Col, Card, Button } from "react-bootstrap";
import { useNavigate } from "react-router-dom";
import { useCakeStore } from "../store/cakeStore";
const AllCakes = () => {
const allCakes = useCakeStore((state) => state.cakesData);
const callGetAPI = useCakeStore((state) => state.getApi);
const navigate = useNavigate();
useEffect(() => {
if (allCakes.length == 0) {
callGetAPI();
}
}, []);
return (
<>
<Container className="mt-2">
<Row>
<Col className="col-md-4 offset-md-4">
<Button
variant="primary"
type="button"
onClick={() => navigate("/add-cake")}
>
Add
</Button>
</Col>
</Row>
<Row xs={1} md={3} className="g-4">
{allCakes.map((cake) => (
<Col key={cake.id}>
<Card>
<Card.Img
variant="top"
src={cake.imageUrl}
style={{ height: 400, width: "100%" }}
/>
<Card.Body>
<Card.Title>{cake.name}</Card.Title>
<Card.Text>Price - {cake.cost}</Card.Text>
</Card.Body>
</Card>
</Col>
))}
</Row>
</Container>
</>
);
};
export default AllCakes;
- (Line: 9) Declare the 'useNavigate()' variable.
- (Line: 12-14) Here get API call only invokes if the data in the state is empty.
- (Line: 21-27) The 'Add' button navigates to the 'AddCake' component.
src/pages/EditCake.js:
const EditCake = () => {
return <></>;
};
export default EditCake;
Configure the route for the 'EditCake' component in the 'App' component.src/App.js:
import { Route, Routes } from "react-router-dom";
import "./App.css";
import Layout from "./components/shared/Layout";
import AddCake from "./pages/AddCake";
import AllCakes from "./pages/AllCakes";
import EditCake from "./pages/EditCake";
function App() {
return (
<Layout>
<Routes>
<Route path="/" element={<AllCakes />}></Route>
<Route path="/add-cake" element={<AddCake />}></Route>
<Route path="/edit-cake/:id" element={<EditCake />}></Route>
</Routes>
</Layout>
);
}
export default App;
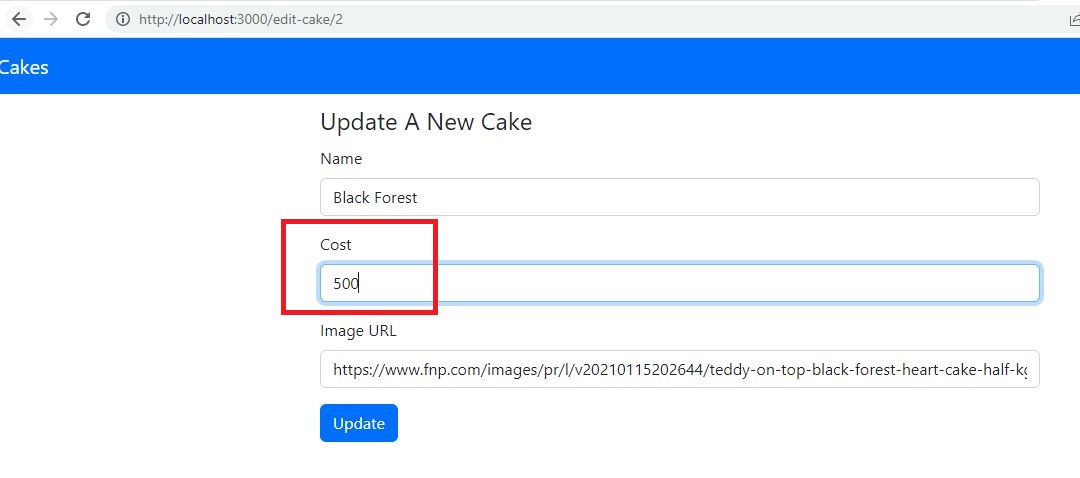
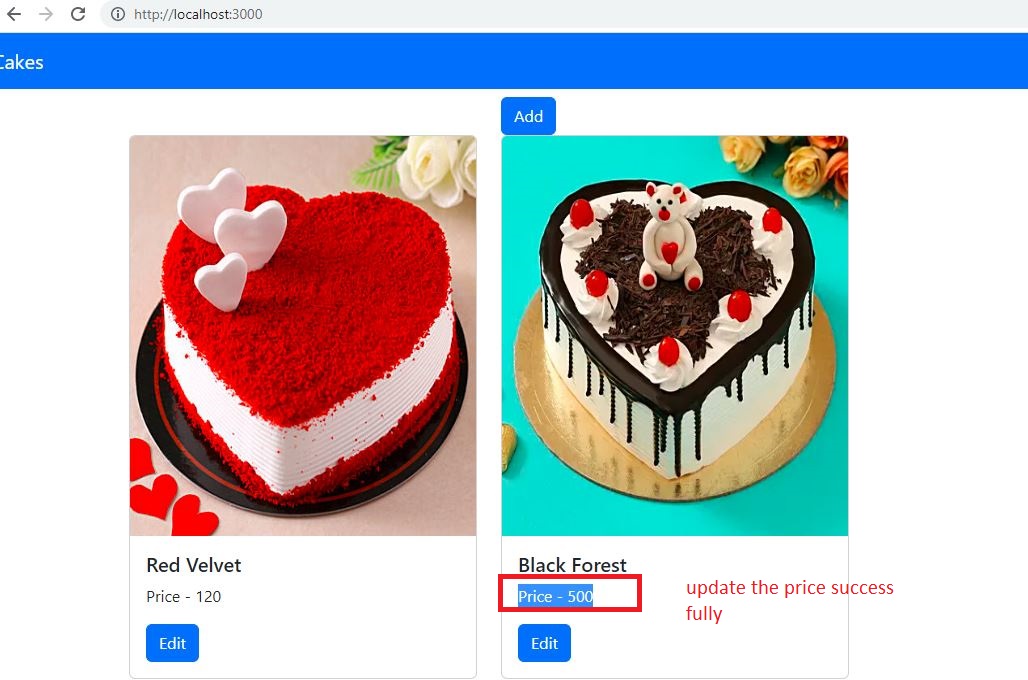
Implement Update Operation:
Let's implement the update operation to update an item and then update our zustand store.
Let's update the logic in the 'carStore.js' file.
src/store/carStore.js:
import create from "zustand";
import { devtools } from "zustand/middleware";
import { immer } from "zustand/middleware/immer";
import axios from "axios";
export const useCakeStore = create(
devtools(
immer((set) => ({
cakesData: [],
getApi: async () => {
const apiResponse = await axios.get("http://localhost:4000/cakes");
set((state) => {
state.cakesData = apiResponse.data;
});
},
createCakeAPI: async (payload) => {
const apiResponse = await axios.post(
"http://localhost:4000/cakes",
payload
);
set((state) => {
state.cakesData.push(apiResponse.data);
});
},
updateCakeAPI: async (payload) => {
const apiResponse = await axios.put(
`http://localhost:4000/cakes/${payload.id}`,
payload
);
set((state) => {
let cakeState = state.cakesData.filter((_) => _.id !== payload.id);
cakeState.push(apiResponse.data);
state.cakesData = cakeState;
});
},
}))
)
);
export const getcakeById = (id) => {
return (state) => {
let cake = state.cakesData.filter((c) => c.id === Number(id));
if (cake) {
return cake[0];
}
return null;
};
};
- (Line: 25-35) Invoking the update API call. Remove the old data of the item from the store and then push the API response into the store state.
- (Line: 40-48) Here 'getCakeById' is our selector to get the item from the state by 'id' value. So this selector is used to fetch the item to edit and then bind it to our edit form.
src/pages/EditCake.js:
import { useEffect } from "react";
import { useNavigate, useParams } from "react-router-dom";
import { getcakeById, useCakeStore } from "../store/cakeStore";
import { useRef } from "react";
import { Col, Container, Row, Form, Button } from "react-bootstrap";
const EditCake = () => {
const name = useRef("");
const imageUrl = useRef("");
const cost = useRef("");
const { id } = useParams();
const cakeToEdit = useCakeStore(getcakeById(id));
const updateAPICall = useCakeStore((state) => state.updateCakeAPI);
const navigate = useNavigate();
useEffect(() => {
if (cakeToEdit) {
name.current.value = cakeToEdit.name;
imageUrl.current.value = cakeToEdit.imageUrl;
cost.current.value = cakeToEdit.cost;
}
}, []);
const updateHandle = async () => {
let payload = {
name: name.current.value,
imageUrl: imageUrl.current.value,
cost: Number(cost.current.value),
id: Number(id),
};
await updateAPICall(payload);
navigate("/");
};
return (
<>
<Container className="mt-2">
<Row>
<Col className="col-md-8 offset-md-2">
<legend>Update A New Cake</legend>
<Form.Group className="mb-3" controlId="formName">
<Form.Label>Name</Form.Label>
<Form.Control type="text" ref={name} />
</Form.Group>
<Form.Group className="mb-3" controlId="formCost">
<Form.Label>Cost</Form.Label>
<Form.Control type="text" ref={cost} />
</Form.Group>
<Form.Group className="mb-3" controlId="formImageUrl">
<Form.Label>Image URL</Form.Label>
<Form.Control type="text" ref={imageUrl} />
</Form.Group>
<Button variant="primary" type="button" onClick={updateHandle}>
Update
</Button>
</Col>
</Row>
</Container>
</>
);
};
export default EditCake;
- (Line: 7-9) Declared the 'useRef' variables to fetch the form data.
- (Line: 10) Read the item to edit value from the URL using 'useParams'.
- (Line: 11) Here we use our selector 'getCakeById' to fetch the item from the store state.
- (Line: 12) Get the store action method reference that invokes the update API call.
- (Line: 16-20) Populate the item to edit to our 'useRef' variables.
- (Line: 23-32) The 'updateHandle' method consists of logic to invoke the update API call sending our form data as payload.
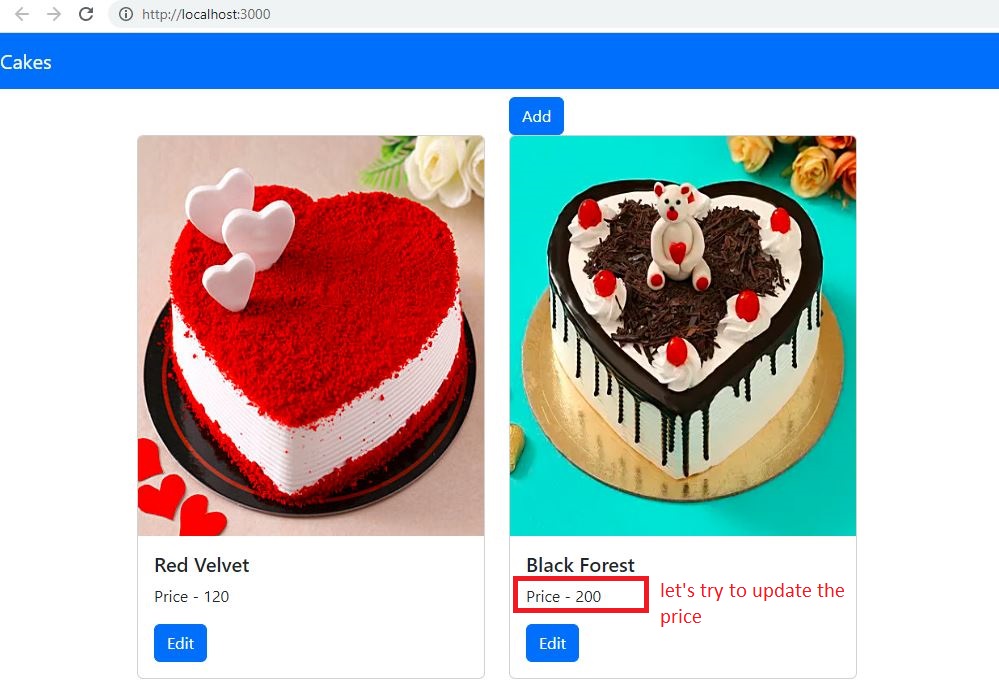
src/pages/AllCake.js:
<Card.Body>
<Card.Title>{cake.name}</Card.Title>
<Card.Text>Price - {cake.cost}</Card.Text>
<Button
variant="primary"
onClick={() => navigate(`/edit-cake/${cake.id}`)}
>
Edit
</Button>
</Card.Body>
(Step 1)(Step 2)
(Step 3)
Create React Component 'DeleteConfirmation':
Let's create a new react component like 'DeleteConfirmation' in the 'components/shared' folder.
src/components/shared/DeleteConfirmation.js:
import Button from "react-bootstrap/Button";
import Modal from "react-bootstrap/Modal";
const DeleteConfirmation = (props) => {
return (
<>
<Modal
show={props.showModal}
onHide={() => {
props.closeDeleteConfirmationModalHandler();
}}
>
<Modal.Header closeButton>
<Modal.Title>{props.title}</Modal.Title>
</Modal.Header>
<Modal.Body>{props.body}</Modal.Body>
<Modal.Footer>
<Button
variant="secondary"
onClick={() => {
props.closeDeleteConfirmationModalHandler();
}}
>
Close
</Button>
<Button
variant="danger"
onClick={() => {
props.confirmDeleteHandler();
}}
>
Confirm Delete
</Button>
</Modal.Footer>
</Modal>
</>
);
};
export default DeleteConfirmation;
- (Line:7) The 'show' property accepts the boolean value 'true' for display and 'false' for hiding modal.
- (Line: 8-10) The 'onHide' event raises by the 'x' button(close button on top right corner). Registered with the parent component method like 'props.closeDeleteConfirmationModalHandler'.
- (Line: 25-32) The 'Confirm Delete' button invokes the delete API call.
Implement Delete Operation:
Let's implement the delete API call in 'cakeStore.js'.
src/store/cakeStore.js:
import create from "zustand";
import { devtools } from "zustand/middleware";
import { immer } from "zustand/middleware/immer";
import axios from "axios";
export const useCakeStore = create(
devtools(
immer((set) => ({
cakesData: [],
getApi: async () => {
const apiResponse = await axios.get("http://localhost:4000/cakes");
set((state) => {
state.cakesData = apiResponse.data;
});
},
createCakeAPI: async (payload) => {
const apiResponse = await axios.post(
"http://localhost:4000/cakes",
payload
);
set((state) => {
state.cakesData.push(apiResponse.data);
});
},
updateCakeAPI: async (payload) => {
const apiResponse = await axios.put(
`http://localhost:4000/cakes/${payload.id}`,
payload
);
set((state) => {
let cakeState = state.cakesData.filter((_) => _.id !== payload.id);
cakeState.push(apiResponse.data);
state.cakesData = cakeState;
});
},
deleteCakeAPI: async (id) => {
const apiResponse = await axios.delete(
`http://localhost:4000/cakes/${id}`
);
set((state) => {
state.cakesData = state.cakesData.filter((_) => _.id !== id);
});
},
}))
)
);
export const getcakeById = (id) => {
return (state) => {
let cake = state.cakesData.filter((c) => c.id === Number(id));
if (cake) {
return cake[0];
}
return null;
};
};
- (Line: 36-43) Delete API call. On API success item has to be removed from the store state as well.
import { useEffect, useState } from "react";
import { Container, Row, Col, Card, Button } from "react-bootstrap";
import { useNavigate } from "react-router-dom";
import DeleteConfirmation from "../components/shared/DeleteConfirmation";
import { useCakeStore } from "../store/cakeStore";
const AllCakes = () => {
const allCakes = useCakeStore((state) => state.cakesData);
const callGetAPI = useCakeStore((state) => state.getApi);
const navigate = useNavigate();
const [showModal, setShowModal] = useState(false);
const [itemIdToDelete, setItemIdToDelete] = useState(0);
const callDeleteAPI = useCakeStore((state) => state.deleteCakeAPI);
useEffect(() => {
if (allCakes.length == 0) {
callGetAPI();
}
}, []);
const openDeleteConfirmationModalHandler = (id) => {
setItemIdToDelete(id);
setShowModal(true);
};
const closeDeleteConfirmationModalHandler = () => {
setItemIdToDelete(0);
setShowModal(false);
};
const confirmDeleteHandler = async () => {
await callDeleteAPI(itemIdToDelete);
setItemIdToDelete(0);
setShowModal(false);
};
return (
<>
<DeleteConfirmation
showModal={showModal}
title="Delete Confirmation"
body="Are you sure to delete the item?"
closeDeleteConfirmationModalHandler={
closeDeleteConfirmationModalHandler
}
confirmDeleteHandler={confirmDeleteHandler}
></DeleteConfirmation>
<Container className="mt-2">
<Row>
<Col className="col-md-4 offset-md-4">
<Button
variant="primary"
type="button"
onClick={() => navigate("/add-cake")}
>
Add
</Button>
</Col>
</Row>
<Row xs={1} md={3} className="g-4">
{allCakes.map((cake) => (
<Col key={cake.id}>
<Card>
<Card.Img
variant="top"
src={cake.imageUrl}
style={{ height: 400, width: "100%" }}
/>
<Card.Body>
<Card.Title>{cake.name}</Card.Title>
<Card.Text>Price - {cake.cost}</Card.Text>
<Button
variant="primary"
onClick={() => navigate(`/edit-cake/${cake.id}`)}
>
Edit
</Button>
<Button
variant="danger"
type="button"
onClick={() => {
openDeleteConfirmationModalHandler(cake.id);
}}
>Delete</Button>
</Card.Body>
</Card>
</Col>
))}
</Row>
</Container>
</>
);
};
export default AllCakes;
- (Line: 11) The 'useState' variable 'showModal' is used for displaying or hiding the modal
- (Line: 12) The 'useState' variable 'itemIDToDelete' for holding the 'id' value of the item to be deleted.
- (Line: 13) The 'callDeleteAPI' holds the delete API call method reference from the store.
- (Line: 21-23) The 'openDeleteConfirmationModalHandler' method gets invoked to show the modal. Here we set value like item 'id' to delete to 'itemIDToDelete' variable and 'true' value to 'showModal' variable.
- (Line: 26-29) The 'closeDeleteConfirmationModalHandler' method gets invoke to hide the modal.
- (Line: 31-35) The 'confirmDeleteHandler' invokes our delete API call.
Support Me!
Buy Me A Coffee
PayPal Me
Video Session:
Wrapping Up:
Hopefully, I think this article delivered some useful information on the ReactJS(v18) CRUD sample using Zustand State Management Library. I love to have your feedback, suggestions, and better techniques in the comment section below.
%20%20Zustand%20State%20Management%20Library%20%20CRUD%20Example.png)


Comments
Post a Comment