A CRUD Operation Demo With Blazor WebAssembly(.NET6) + Strawberry Shake GraphQL Client + MudBlazor UI + GraphQL API
In this article, we are to implement CRUD operation in Blazor WebAssembly(.NET6) by consuming GraphQL endpoint with help of 'Strawberry Shake'(Graphql Client Library).
Now install the Strawberry Shake CLI tool.
Add the 'Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection' NuGet.
In '.graphqlrc.json' file add the namespace property so that 'Client class' generated by the schema will use it.Now add the same namespace into the '_Import.raozr'.
Now register our 'Client class' based HttpClient instance in the 'Program.cs'.
Now let's create a new blazor component like 'AddOrUpdateCakeDialog.razor' that acts as MudBlazor Dialog component.
GraphQL Endpoint:
In this demo, we have to consume the GraphQL endpoint from our Blazor WebAssembly application.
Source code for .Net6 GraphQL CRUD operations.
The article explains about creating .NET 6 GraphQL CRUD operations
The video explains about creating .NET6 GraphQL CRUD operations
The article explains about creating .NET 6 GraphQL CRUD operations
The video explains about creating .NET6 GraphQL CRUD operations
Strawberry Shake:
Strawberry shake is an open-source GraphQL client that is compliant with the newest GraphQL draft spec, which makes Strawberry Shake compatible with all GraphQL compliant servers like Hot Chocolate, Apollo Server, GraphQL Java, and various other servers out there.
Strawberry Shake will generate the schema of GraphQL Server which will help to invoke the GraphQL endpoint very easily.
Strawberry Shake CLI Tool:
Strawberry shake CLI needs to be configured because CLI will help us to generate the GraphQL client.
Create a folder where we are going to add our Blazor server application. In the same folder open the command prompt and run the below commands to configure the Strawberry Shake CLI.
Create a dotnet tool-manifest
dotnet new tool-manifest
Now install the Strawberry Shake CLI tool.
dotnet tool install StrawberryShake.Tools --local
Create A Blazor WebAssembly Application:
Let's create a Mudblazor template Balzor WebAssembly(.NET6) application. So using Mudblazor commands we can create a built-in templated project very easily without any external configuration.
Install Mudblazor Template into our system.
dotnet new --install MudBlazor.Templates
Now run the below command to create Blazor WebAssembly(.NET6) application along with default Mudblazor UI configuration.
dotnet new mudblazor --host wasm --name YourProjectName
Now run the project and the application looks as below.
Install Required NuGet Package:
Add the 'StrawberryShake.Transport.Http' NuGet.
Package Manager Command
Install-Package StrawberryShake.Transport.Http -Version 12.6.0
Install-Package StrawberryShake.Transport.Http -Version 12.6.0
.NET CLI Command
dotnet add package StrawberryShake.Transport.Http --version 12.6.0
dotnet add package StrawberryShake.Transport.Http --version 12.6.0
Add the 'StrawberryShake.CodeGeneration.CSharp.Analyzers' NuGet.
Package Manager Command
Install-Package StrawberryShake.CodeGeneration.CSharp.Analyzers -Version 12.6.0
Install-Package StrawberryShake.CodeGeneration.CSharp.Analyzers -Version 12.6.0
.NET CLI Command
dotnet add package StrawberryShake.CodeGeneration.CSharp.Analyzers --version 12.6.0
dotnet add package StrawberryShake.CodeGeneration.CSharp.Analyzers --version 12.6.0
Add the 'Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection' NuGet.
Package Manager Command
Install-Package Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection -Version 6.0.0
Install-Package Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection -Version 6.0.0
.NET CLI Command
dotnet add package Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection --version 6.0.0
dotnet add package Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection --version 6.0.0
Add the 'Microsoft.Extensions.Http' NuGet.
Package Manager Command
Install-Package Microsoft.Extensions.Http -Version 6.0.0
Install-Package Microsoft.Extensions.Http -Version 6.0.0
.NET CLI Command
dotnet add package Microsoft.Extensions.Http --version 6.0.0
dotnet add package Microsoft.Extensions.Http --version 6.0.0
Generate GraphQL Client Using GraphQL Server Schema:
Strawberry Shake helps to generate a lot of boilerplate code like 'Schema'(Generates Server GraphQL schema into our blazor application), 'GraphQL Client'(this client class generated based on the schema, this client class contains all resolver methods of our server endpoint).
Now make sure our GraphQL endpoint server running.
Now let's run the Strawberry Shake command to generate the 'Schema'
dotnet graphql init https://YourDomain/graphql/ -n YourClientName -p ./YourFolderName
- 'YourClientName' - Specify any name this will be used to generate a client class that will contain all predefined methods consuming the GraphQL endpoint.
- 'YourFolderName' - Specify any name, a folder will be created that contains files like below.
@using Dot6.StrawberyShake.Crud.Demo.CakeGqlSchema
Read Operation:
Now from the Blazor WebAssembly application, we have to invoke the GraphQL query to fetch all data.
Now inside of our schema generate folder let's add a file like 'GetAllCakes.graphql'.
CakeGqlSchema/GetAllCakes.graphql:
query GetAllCakes{
allCakes{
id
name
description
price
}
}
- (Line: 1) The 'GetAllCakes' is the custom name. In a real GraphQL server query, we won't add, but here we add because using this naming method will be created inside of the 'Client Class'.
- Here is the GraphQL query for fetching the collection of 'Cakes' from the server.
Program.cs:
builder.
Services.
AddCakeGql()
.ConfigureHttpClient(
client => client.BaseAddress = new Uri("https://localhost:7177/graphql/"));
- The 'AddCakeGql()' method generated base on our 'Client class' name.
- Here we configure our Server GraphQL endpoint.
Dtos/Cake.Dto.cs:
namespace Dot6.StrawberyShake.Crud.Demo.Dtos;
public class CakeDto
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public decimal Price { get; set; }
public string Description { get; set; }
}
Let's update our 'Index.razor' component to bind our sample GraphQL endpoint data.Pages/Index.razor:(Html Part)
@page "/"
@inject CakeGql _cakeGql;
<MudGrid Justify="Justify.Center" class="pr-4 pl-4">
@foreach (var cake in allCakes)
{
<MudItem xs="3">
<MudCard>
<MudCardHeader>
<CardHeaderContent>
<MudText Typo="Typo.body1">@cake.Name</MudText>
<MudText Typo="Typo.h6">@cake.Price $</MudText>
</CardHeaderContent>
</MudCardHeader>
<MudCardContent>
<MudText Typo="Typo.body2">@cake.Description</MudText>
</MudCardContent>
<MudCardActions>
<MudIconButton Icon="@Icons.Filled.Edit" Color="Color.Primary" />
<MudIconButton Icon="@Icons.Filled.Delete" Color="Color.Error" />
</MudCardActions>
</MudCard>
</MudItem>
}
</MudGrid>
- (Line: 2) The 'CakeGql' (Client class generated by the Strawberry Shake) was injected into our 'Index.razor'.
- (Line: 4) Looping the GraphQL API response data.
- (Line: 10&11&15) Binding the GraphQL API response data.
@code {
List<CakeDto> allCakes = new List<CakeDto>();
protected override async Task OnInitializedAsync()
{
var result = await _cakeGql.GetAllCakes.ExecuteAsync();
allCakes = result.Data.AllCakes.Select(c => new CakeDto
{
Description = c.Description,
Id = c.Id,
Name = c.Name,
Price = c.Price
}).ToList();
}
}
- (Line: 2) Initialized 'CakeDto' collection.
- (Line: 3) The 'OnInitializedAsync' is a life cycle method in which we will invoke our GraphQL endpoint.
- (Line: 5) The 'GetAllCakes' property created by the query 'CakeGqlSchema/GetAllCake.graphql'. The 'ExecuteAsync()' method triggers the GraphQL call.
- (Line: 6-12) Fetching the response data. Here we can observe 'result.Data.AllCakes' means 'Data' is the parent property, 'AllCakes'(this name depended up on your server GraphQL resolver method name) is child property.
Create Operation:
Let's try to implement the create operation by sending a mutation request to the GraphQL endpoint.
In the 'CakeGqlSchema' folder let's add our mutation file like 'CreateCake.graphql'.
CakeGqlSchema/CreateCake.graphql:
mutation CreateCake($newCake:CakeInput!){
saveCake(newCake:$newCake) {
id
}
}
- Here 'CreateCake' in normal Graphql mutation we won't add but here we add because strawberry shake library used this name to create method in the 'CakeGql'(Client class generated by strawberry shake).
Note:- Once 'CreateCake.graphql' file is added run the build command so that 'CakeGql' get refreshed with new methods related to the files we created
Pages/AddOrUpdateCakeDialog.razor:(Html Part)
<MudDialog>
<DialogContent>
<MudTextField T="string" Label="Name" @bind-Value="cake.Name" />
<MudTextField T="decimal" Label="Price" @bind-Value="cake.Price" />
<MudTextField T="string" Label="Description" @bind-Value="cake.Description" Lines=4/>
</DialogContent>
<DialogActions>
<MudButton OnClick="Cancel">Cancel</MudButton>
<MudButton Color="Color.Primary" OnClick="Submit">Ok</MudButton>
</DialogActions>
</MudDialog>
- Here rendering MudBlazor Dialog components and creating the form where we can submit the form to create a new item.
@code {
[CascadingParameter] MudDialogInstance MudDialog { get; set; }
[Parameter] public CakeDto cake { get; set; } = new CakeDto();
private void Cancel()
{
MudDialog.Cancel();
}
private void Submit()
{
MudDialog.Close(DialogResult.Ok<CakeDto>(cake));
}
}
- (Line: 2) The 'MudDialogInstance' gives control over the dialog box.
- (Line: 3) The 'CakeDto' was used for form binding and it was decorated with '[Parameter]' which means the component that invoked Dialog can pass the data to the 'CakeDto' instance.
- (Line: 6-9) The 'Cancel' method to close the dialog.
- (Line: 11-14) The 'Submit' method passes the form data to its parent component and then closes the dialog.
Pages/Index.razor:(Html Part)
@page "/"
@inject CakeGql _cakeGql;
@inject IDialogService _dialogService;
<MudContainer Class="d-flex justify-center mb-2">
<MudFab Color="Color.Primary" Icon="@Icons.Material.Filled.Add" Size="Size.Large" IconSize="Size.Large" Label="Add A New
Cake" Class="ma-2" @onclick="(e => CreateAsync())" />
</MudContainer>
<MudGrid Justify="Justify.Center" class="pr-4 pl-4">
<!-- Code hidden for display purpose -->
</MudGrid>
- (Line: 3) Injected the 'IDialogService' instance that helps to interact with MudBlazor Dialog.
- (Line: 5-8) Rendered the 'Add A New Cake' button and its click registered with the 'CreateAsync()' method.
private async Task CreateAsync()
{
var parameters = new DialogParameters();
parameters.Add("cake", new CakeDto());
var dialog = await _dialogService.Show<AddOrUpdateCakeDailog>("Create A Post", parameters).Result;
if (dialog.Data != null)
{
CakeDto newCake = dialog.Data as CakeDto;
var gqlPayload = new CakeInput()
{
Description = newCake.Description,
Id =0,
Name = newCake.Name,
Price = newCake.Price
};
var result = await _cakeGql.CreateCake.ExecuteAsync(gqlPayload);
newCake.Id = result.Data.SaveCake.Id;
allCakes.Insert(0, newCake);
}
}
- (Line: 3) Initialized the 'DialogParameters'.
- (Line: 4) Adding the 'CakeDto' instance as a parameter.
- (Line: 5) Using 'IDialogService.Show()' method opens the popup. For the 'Show()' method first parameter is the title of the Dialog, 2nd parameter of the type 'DialogParameters'.
- (Line: 7) This conditional statement was executed on closing the Dialog. The 'dailog.Data' is empty if we click the 'Cancel' button. The 'dailog.Data' contains form data on clicking the 'Ok' button.
- (Line: 9-17) Here 'CakeInput' type is autogenerated by the Strawberry Shake. The 'CakeInput' is the GraphQL variable type.
- (Line: 19) Invoking the Graphql endpoint by sending mutation requests. The 'CreateCake' property gets created based on the Graphql files added in the 'CakeGqlSchema' folder.
- (Line: 20) Newly created record 'Id'.
- (Line: 22) Newly created record added to the on top of the existing items collection.
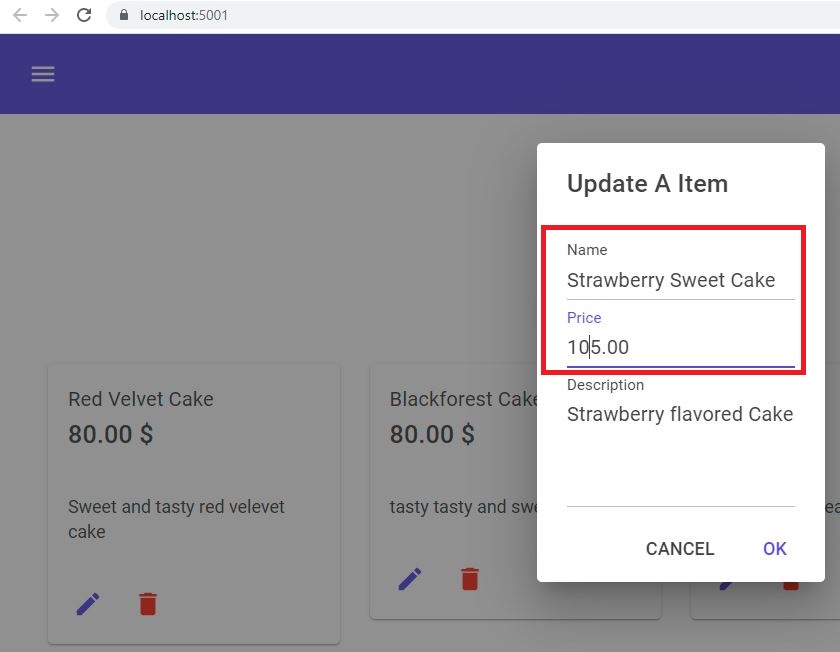
Update Operation:
Let's try to implement the update operation by sending a mutation request to the GraphQL endpoint.
In the 'CakeGqlSchema' folder let's add our mutation file like 'UpdateCake.graphql'.
CakeGqlSchema/UpdateCake.graphql:
mutation ModifyCake($updateCake:CakeInput!){
updateCake(updateCake:$updateCake) {
id
}
}
- Here 'ModifyCake' name will be used by the 'CakeGql'(client generated by the Strawberry Shake).
Now in the 'Index.razor' let's add the update operation logic as follows.
Index.razor:(Html Part)
<MudIconButton Icon="@Icons.Filled.Edit" Color="Color.Primary" @onclick="(e => UpdateAsync(cake.Id))" />
- Here our 'Edit' button click registered with the 'UpdateAsync()' method.
private async Task UpdateAsync(int id)
{
var parameters = new DialogParameters();
var cakeNeedToUpdate = allCakes.FirstOrDefault(_ => _.Id == id);
parameters.Add("cake", cakeNeedToUpdate);
var dialog = await _dialogService.Show<AddOrUpdateCakeDailog>("Update A Item", parameters).Result;
if (dialog.Data != null)
{
var updatedCake = dialog.Data as CakeDto;
var gqlPayload = new CakeInput()
{
Description = updatedCake.Description,
Id =updatedCake.Id,
Name = updatedCake.Name,
Price = updatedCake.Price
};
var result = await _cakeGql.ModifyCake.ExecuteAsync(gqlPayload);
allCakes.Remove(cakeNeedToUpdate);
allCakes.Insert(0, updatedCake);
}
}
- (Line: 4-5) Adding the record to update as the 'DialogParameters' parameter so that data gets populated onto our dialog.
- (Line: 17) Invokes Graphql endpoint and sends mutation request for the updating the data at the server.
Delete Operation:
Let's try to implement the delete operation by sending a mutation request to the GraphQL endpoint.
In the 'CakeGqlSchema' folder let's add our mutation file like 'DeleteCake.graphql'.
CakeGqlSchema/DeleteCake.graphql:
mutation RemoveCake($id:Int!){
deleteCake(id:$id)
}
- Here 'RemoveCake' name will be used by the 'CakeGql'(client generated by the Strawberry Shake).
In the 'Index.razor' component let's add the delete operation logic as follows.
Pages/Index.razor:(Html Part)
<MudIconButton Icon="@Icons.Filled.Delete" Color="Color.Error" @onclick="(e => DeleteAsync(cake.Id))" />
- Here 'Delete' button registered with 'DeleteAsync()' method.
private async Task DeleteAsync(int id)
{
bool? result = await _dialogService.ShowMessageBox(
"Delete Confirmation",
"Deleting can not be undone!",
yesText: "Delete!", cancelText: "Cancel");
if (result ?? false)
{
await _cakeGql.RemoveCake.ExecuteAsync(id);
var cakeToRemove = allCakes.FirstOrDefault(_ => _.Id == id);
allCakes.Remove(cakeToRemove);
}
}
- (Line: 3-7) Using the 'IDialogService' display a small delete confirmation dialog.
- (Line: 8) The 'result' value will be 'null' on clicking the 'Cancel' button, the 'result' value will be 'true' on clicking the 'Delete' button.
- (Line: 10) Invokes the GraphQL endpoint and sends a mutation request for deleting an item.
Support Me!
Buy Me A Coffee
PayPal Me
Video Session:
Wrapping Up:
Hopefully, I think this article delivered some useful information on a basic CRUD operation in Blazor WebAssembly with Strawberry Shake Library for consuming GraphQL endpoint. I love to have your feedback, suggestions, and better techniques in the comment section below.
.png)



















Great blog. So thorough. You have mastered Hot Chocolate and Strawberry Shake. Can you please upload the finished working code for this blog to GitHub?
ReplyDeleteThank you so much for this post. The docs on Strawberry Shake is sketchy at best, so this is great!
ReplyDeletei migrated my project to .net7 and strawberryshake 13, and it seem the mutation aint calling the api side. the queries and the signalR is working fine though
ReplyDelete